Introduction
Did you know that there are over 100,00 posts on Instagram for the #biotin?
Biotin is claimed to promote healthy hair, strong nails and glowing youthful skin. It is also touted as a cure-all for brain, heart and endocrine health.
The impulsive side of me shouts 'Sign me up for biotin right now'.
The more logical part suspects that this might just be an e-myth just waiting to be debunked.
What Is Biotin?
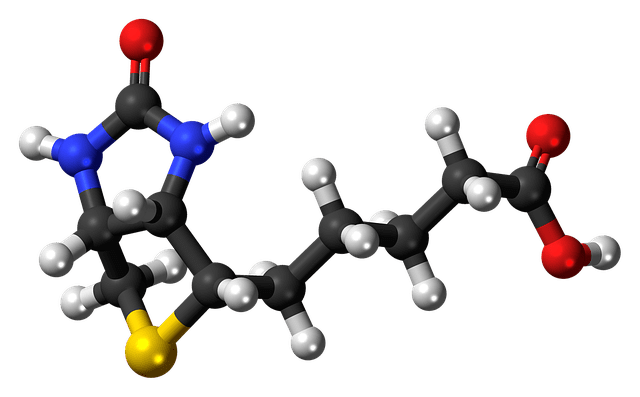
Biotin is a water soluble B vitamin. It is also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H. It is composed of a ureido ring fused with a tetrahydrothiophene ring.
Biotin plays a vital role as a co-factor in key metabolic processes eg metabolism of carbohydrate and fat.
In 1936, a substance was identified in egg yolk that was necessary for yeast growth and was termed biotin.Biotin is distributed unequally across cellular compartments. The majority of biotin is located in the mitochondria and cytoplasm with lower concentration in the cell nucleus and microsomes.
Biotin deficiency is rare but is seen in severely malnourished children in the developing world.
It is also seen in people who consume large amounts of raw egg whites as egg whites contain avidin which binds to biotin.
Low levels of biotin may be seen in people who consume large amounts of alcohol.
It is estimated that 50% of pregnant women in the USA have marginal biotin deficiency.
Signs of biotin deficiency include:
- perioral facial dermatitis
- conjunctivitis
- alopecia (lack of hair)
- ataxia (lack of balance)
- hypotonia (weak reflexes)
- ketoacidosis skin infections and
- developmental delay.
There are over 4000 biotin related products for sale on Amazon including capsules, lotions, potions and shampoos. You can spend several hundred dollars on some of these biotin products.
Can You Get Biotin From Food?
Mammals cannot synthesize biotin and depend on intake from microbial and plant sources.
The daily adequate intake of biotin is 30 mcg in adults. In general, biotin exists bound to protein and is known as biocytin, It need to undergo proteolysis to release free biotin. As an example, most grains have a 20 – 40 % bioavailablity of biotin (meaning how much is absorbed). The biotin in corn does not need to undergo proteolysis and is readily available.
Food rich in biotin include: (content per 100 gms):
- maitake mushroom (dried) 24 mcg
- eggs 19 mcg
- chicken liver 188 mcg
- soybeans 180 mcg
- peacans 27 mcg
- almonds 60 mcg
- butter 94 mcg.
Is There Any Research?
There are 30,000 publications relating to biotin including 218 clinical trials. This compares favourably to vitamin B6 or B12 which have similar numbers of publications and clinical trials.
Does Biotin Support A Healthy Metabolism & Glucose Levels?
A total of 447 patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes were randomized to receive chromium plus biotin of placebo for 90 days in addition to their usual anti diabetic medication (1).
There was a statistically significant difference in the HbA1C (long term measure of glucose control) between the two arms in favour of the active arm of the study.
A double blind placebo controlled trial of biotin was carried out in 40 middle aged/elderly men over 71 days. (A very odd choice of days for a clinical study). The study subjects were randomized to either biotin (0.9mg/day) or placebo (2). Plasma biotin levels were elevated by biotin supplementation and there was a negative correlation between biotin levels and total plasma lipids.
Similar results were found in a 4 week study from Connecticut where the combination of chromium plus biotin (in addition to standard of care) improved both glucose and lipids levels in 43 subjects with impaired glycemic control (3).
A single study from 1980 looked at the effects of biotin on lipids in healthy men and women but neither the abstract nor paper is available on Pubmed.
Bottom Line
There is very limited short-term information on biotin supplementation (usually plus chromium) on metabolism and glucose control in high-risk patients. However there is no reliable information on biotin supplementation in healthy men and women.
Does It Maintain Healthy Skin Hair and Nails?

There is only on clinical trial looking at biotin and hair. It was done in Poland in 1966 (before I was born) and there is no abstract or summary available any more (4)
Apart from this, there are a few case reports of biotin for the ‘uncombable hair syndrome’. I had never heard of this until I found these papers but have often thought that I might suffer from something similar).
Apparently, ‘uncombable hair syndrome’ is an autosomal;a dominant condition which presents as’ unruly dry blonde hair with a tangles appearance’. (Yes, that’s me to a tee). Affected people often also have brittle nails. A trial of oral biotin 5mg/day in 2 people over two years was done (5).
Yes, I said two people. Following two years of biotin supplementation, these two people reported more manageable hair which was maintained even after discontinuation of the biotin. Nails also improved but required on going biotin supplementation to maintain this improvement.
It is staggering to think that the multi-million dollar biotin cosmeceutical industry is based on just 2 people.
Bottom Line
There is no credible science to support biotin for healthy skin and nails.
Does it Help The Brain?
There are no human clinical trials evaluating biotin for cognitive decline. The only studies of interest relating to the central nervous system can be divided into two main groups:
- Infantile encephalopathies
and
2. Multiple Sclerosis
Infantile encephalopathies
There are a specific group of rare metabolic encephalopathies e.g
- biotinidase
- holocarboxylase synthetase
- Leigh encephalopathy
which present in childhood and respond to biotin supplementation (6)
There are also conflicting results on the use of biotin responsive basal ganglia disease in aa rare syndrome known as basal ganglia (7)
A single case report from Verona, Italy, describes a dramatic improvement in an infant with encephalopathy and a seizure disorder with biotin 5mg/day (8)
Multiple sclerosis
A pilot proof of concept study looked at the effect of high dose biotin in 23 patients with multiple sclerosis (9). Judgement criteria varied according to clinical presentations. Preliminary data suggest that high doses of biotin might have an impact on disability and progression in progressive multiple sclerosis.
Bottom Line
There is no research to support a role for biotin in brain health in the general population.
Does It Affect Cardio Vascular Health?
There are no human clinical trials looking at biotin for cardiovascular health. As mentioned earlier, a study in diabetic patients showed improved lipid profiles. Other than that, the main significance of biotin relates to the safety of laboratory tests for patients with acute coronary syndrome.
Biotin may cause a false low troponin level and troponin is used as part of a decision matrix to diagnose myocardial infarction. Additionally, biotin can affect the diagnosis of cardiac failure and the levels of the medication digoxin, in the blood (10).
Bottom Line
Biotin does not promote heart health.
Does It Affect The Thyroid Or Adrenal Function?
Biotin supplementation can affect the results of laboratory tests for thyroid, heart failure, myocardial infarction, pregnancy and cancer. Up to two thirds of common laboratory tests may be falsely negative or positive in patients taking biotin supplementation.
Bottom Line
There are no clinical trials looking at biotin for thyroid disease. The only relevant publication relate to false positive and false negative thyroid function tests in patients who were taking biotin supplementation (11)
Does It Affect Muscle or Tissue Repair?
Oral administration of biotin 1mg/day to 14 patients with muscle cramps related to hemodialysis resulted in improvements in the severity of the cramps in 12 of the patients (12).
Dialysis patients are a very unique subset of the general population and we cannot extrapolate results to other demographics.
Bottom Line
Biotin does not support muscle or tendon repair in the general population.
Is Biotin Supplementation Safe?
Biotin is generally regarded as safe and there are no clinical case reports of toxicity. However, it is important to let your physician know if you are taking biotin as it can interfere with critical laboratory tests.
Excess biotin can inhibit sirutin activity (proteins that regulate key processes in the body) which could theoretically lead to increased inflammation.
Reconciling The Numbers
As mentioned above, there are 218 clinical studies on biotin. We have used relatively few of these studies in this overview. This begs the question as to what the other papers are about.
Are we missing something?
Many of these unaccounted for studies relate to using biotin as a marker in radiology. As an example, there are 40 studies alone on using avidin-biotin to deliver radiotherapy to tumors.
Conclusion
I find it somewhere between sad and frustrating to think of all the people who view posts on social media claiming that biotin can solve your hair, nail and skin problems.
People who promote biotin for cosmetic reasons should be forced to add the disclaimer:
'These claims are based on the results of one Polish study (that we never read) and 2 people with genetic mutations)."
This industry preys on and profits from the insecurity and unhappiness that is all too prevalent in modern society.
Who would consider buying biotin if they knew the actual truth?
Biotin, you have been officially debunked.

Leave a Reply